



؟What are Incoterms
Incoterms is a combination of three English words (International Commercial Terms) which includes international commercial terms. In other words, Incoterms is a set of commercial rules and regulations used by the International Trade Organization to determine responsibilities and duties, transportation and logistics.
The rules and regulations related to Incoterms include insurance, freight, transportation, logistics, duties, responsibilities, damage. Companies and the country of origin and destination can use Incoterms to specify the transportation rules in detail to avoid any ambiguities.
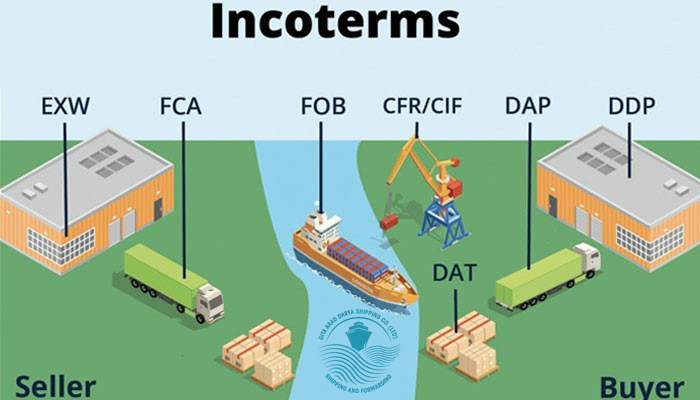
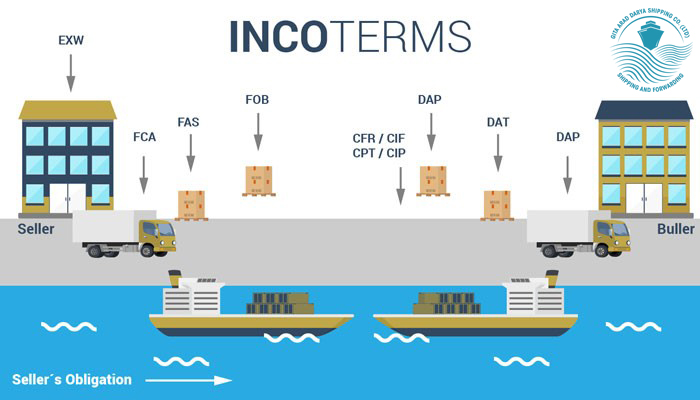
Types of Incoterms
Group E in Incoterms
(Delivery of goods at origin)
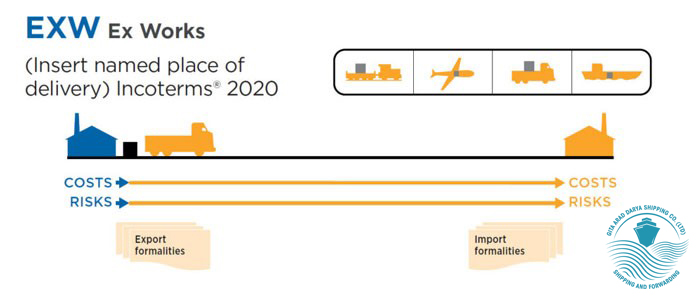
Group F in Incoterms
(delivery of goods to the buyer excluding freight)

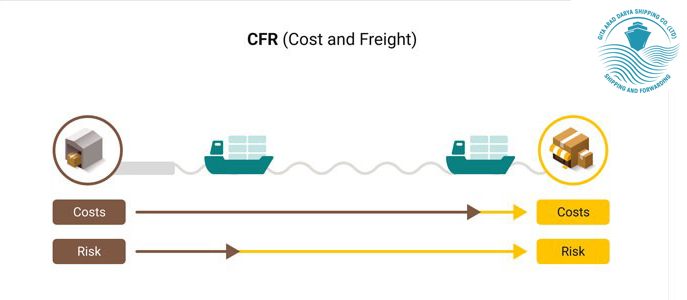
Group C (Delivered at Origin with Freight)
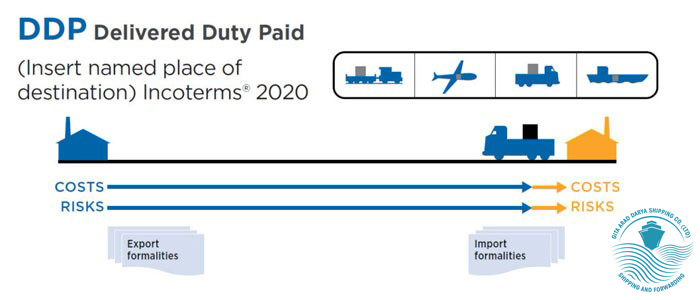
Group D (Delivered at Destination)
Benefits of Incoterms rules
What is the use of Incoterms?
If you are unsure about choosing the desired Incoterm, contact us for guidance!
?What are the consequences of not using Incoterms rules
- The existence of ambiguities: One of the disadvantages of using Incoterms rules in commercial transactions between two sellers and buyers is the creation of ambiguities in determining duties and responsibilities.
- Lack of protection of the interests of both parties: One of the disadvantages of the lack of Incoterms rules is the creation of problems and the failure to protect the interests of the contracting parties.
- The emergence of disputes: Without Incoterms rules, the two parties to commercial transactions may face numerous problems and disputes. Because if there is no common language and specified rules, many ambiguities and problems arise for both sellers and buyers.
- Lack of clarity of responsibility and duties: One of the disadvantages of not using the terms rules is the lack of clarity of the duties and responsibilities of buyers and sellers in commercial transactions. Also, without Incoterms rules, the cost of transportation, freight, insurance and possible damage to the goods cannot be accurately determined.
How to use Incoterms rules
- Choosing an Incoterms rule: You must choose one of the Incoterms rules according to your situation and specify the responsibilities of each buyer and seller in the transaction.
- Conditions: The conditions of transportation of the goods and their details must be explained in full. The type of responsibilities, transportation and its cost, and insurance conditions must be precisely determined.
- Creating an agreement: An agreement must be prepared between the buyer and seller to accept the Incoterms rules and terms, and the details of the responsibilities, including transportation costs and insurance conditions, must be specified in it.
- Implementation: You must implement the Incoterms rules and conditions and each person must fulfill their responsibilities.
- Compliance with Incoterms rules and regulations: You must carefully comply with the Incoterms rules and conditions throughout the contract.
Final Words
Frequently Asked Questions
If you are interested in working with our collection, send your resume!
Gita Arad Darya International Shipping and Transport
This company is proud to improve its position in the field of international transportation services by using its valuable and successful work experiences in the past years and cooperating with reputable domestic and foreign companies and by having experienced and experienced personnel and by complying with quality standards faster than in the past.
- Courses
- Permissions
- Incoterms
Contact us: 02144035001-03 Email: operation@araddarya.com Address of the head office: No. 44, 8th floor, Mina Tower, 2nd floor of Sadeghieh, at the beginning of Ayatole Kashani St., Tehran.
 فارسی
فارسی